The Best Information Gathering Tool: Harvester Hacker’s Favorite in 2025
Discover why Harvester is the top information gathering tool for hackers in 2025. Learn its features, usage, and how it enhances OSINT efforts.
What is Information Gathering Tool Harvester?
Harvester, also known as “theHarvester,” is an open-source intelligence (OSINT)Information gathering tool designed to help security professionals collect information about a target. It can extract data from various public sources, including search engines, social media platforms, and public databases. The tool is particularly useful for gathering email addresses, subdomains, and other valuable information that can aid in reconnaissance during penetration testing.
Why Harvester is a Favorite in 2025
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Harvester can pull data from multiple sources, including Google, Bing, LinkedIn, and more. This capability allows hackers to compile a wealth of information about their targets quickly.
- User -Friendly Interface: The tool is designed with usability in mind. Even those new to hacking can navigate its features with relative ease.
- Regular Updates: The developers of Harvester are committed to keeping the tool up-to-date with the latest changes in data sources and search engine algorithms, ensuring its effectiveness in 2025.
- Integration with Other Tools: Harvester can be easily integrated with other security tools, making it a valuable addition to any hacker’s toolkit.
- Open Source: Being open-source means that the community can contribute to its development, leading to continuous improvements and new features.
How to Use Harvester on Linux
Using Harvester on a Linux system is straightforward. Below, we’ll walk you through the installation process and basic usage.

Step 1: Install Harvester
- Before installing any new software, it’s a good idea to update your package list. Open your terminal and run:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade - Harvester requires Python and some additional libraries. Install them using:
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip git - Download the Harvester tool from its GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/laramies/theHarvester.git - Change into the Harvester directory:
cd the Harvester - Use pip to install the necessary Python packages:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Step 2: Basic Usage of Harvester
Once you have Harvester installed, or you can clone from github you can start using it to gather information. Here are some basic commands to get you started:

- Basic command
python3 theHarvester.py -d <domain> -b <source>-d: Specifies the target domain.-b: Specifies the data source (e.g., google, bing, linkedin).
- To gather information about the domain
example.comusing Google, you would run:python3 theHarvester.py -d example.com -b google - You can also specify multiple sources to gather more comprehensive data:
python3 theHarvester.py -d example.com -b google -b bing -b linkedin - Harvester allows you to save the results in various formats. To save the output in a text file, use:
python3 theHarvester.py -d example.com -b google -f output.txt - Harvester comes with several advanced options, such as specifying the number of results to return, using API keys for certain sources, and more. You can view all available options by running:
python3 theHarvester.py -h

How hackers use this tool
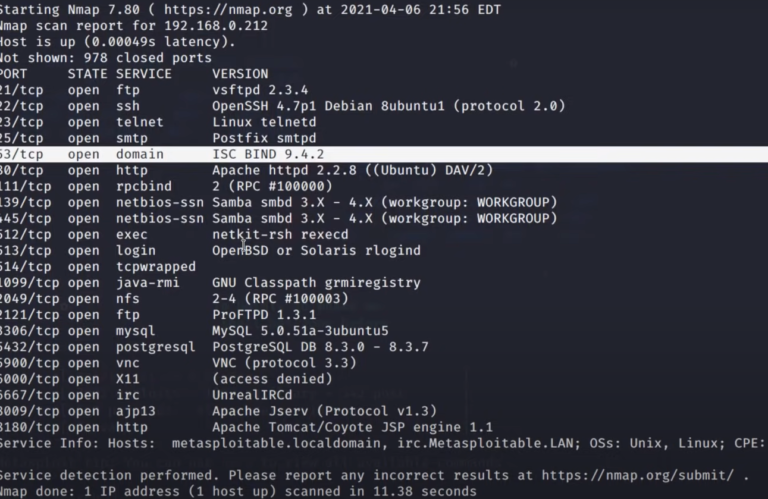
Hackers use the Information Gathering Tool Harvester tool in Linux to gather open-source intelligence (OSINT) about their targets. By extracting information such as email addresses, subdomains, and employee names from various public sources like search engines and social media, they can compile valuable data for reconnaissance during penetration testing or malicious activities.
1. Information Gathering
- Email Collection: Hackers can extract email addresses associated with a target domain, which can be used for phishing attacks or social engineering.
- Subdomain Discovery: By identifying subdomains, hackers can uncover additional attack surfaces that may be less secure than the main domain.
- Hostnames and IP Addresses: The tool helps in mapping domain names to their corresponding IP addresses, which is crucial for further network scanning and vulnerability assessments.
2. Reconnaissance Phase
- Understanding Target Footprint: During the reconnaissance phase of a penetration test, hackers use Harvester to understand the digital footprint of a target organization, including its online presence and potential vulnerabilities.
- Identifying Weak Points: By gathering information about employees and their roles, hackers can identify potential weak points in the organization’s security posture.
3. Utilizing Multiple Data Sources
- Diverse Search Engines: Hackers can query multiple search engines (e.g., Google, Bing, Yahoo) and databases (e.g., PGP key servers, SHODAN) to gather comprehensive data about the target.
- API Integration: For enhanced results, hackers can configure API keys for services like Hunter.io, allowing them to gather professional email addresses tied to the domain.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of cybersecurity in 2025, Information Gathering Tool like Harvester play a pivotal role in the information gathering tool of ethical hacking. Its ability to compile data from various sources quickly and efficiently makes it a favorite among hackers. However, it’s essential to remember that with great power comes great responsibility. Always use such tools ethically and within the bounds of the law.





Hi Techweapon 01,
Let’s face it—most marketing strategies today are ineffective, leaving business owners frustrated and wondering where all their money went.
Here’s the truth: Traditional marketing doesn’t work anymore. It’s about time to shift to direct-response marketing, the proven strategy that generates results in the real world.
Dan Kennedy, one of the leading marketing experts, swears by direct-response marketing, and his strategies have helped thousands of business owners grow their brands.
Let me show you how to apply it to your business.
Step 1: Know Your Target Audience
Targeting everyone is a huge mistake. You must define your ideal customer. Direct-response marketing requires you to speak directly to a specific group of people.
Example 1:
Target Audience: Busy professionals
Offer: “Quick and effective workout plans for busy professionals.”
This specific focus allows businesses to craft marketing messages that truly resonate.
Example 2:
Target Audience: Aspiring entrepreneurs
Offer: “The ultimate guide to start your e-commerce store in 30 days—no prior experience required.”
This appeals directly to the desires of this niche, making the marketing message much stronger.
Step 2: Clear and Compelling Offer
A great product is only as good as the offer. The offer should solve a problem and make it impossible for your ideal customer to say no.
Example 1:
A fitness coach offered: “Sign up for my program today and receive a free 1-hour coaching session, valued at $300.” This added value made the offer irresistible.
Example 2:
An e-commerce store offered: “Free shipping on all orders over $50, plus a free product with every purchase.” The free bonus added to the deal makes it more attractive.
Step 3: Track Everything
If you’re not measuring, you’re guessing. The most successful marketers track their results religiously.
Example 1:
A car dealership tested their email campaigns and found that subject lines with specific car models drove a 25% higher open rate than generic ones.
Example 2:
A SaaS company split their traffic between two landing pages: one with a video and one with text. The video version converted 40% more visitors into paying customers.
Your Action Step:
Start tracking your marketing results—whether it’s email opens, clicks, or conversions. If you don’t track, you can’t improve.
Tomorrow, we’ll dive into crafting irresistible offers and how to create something your customers can’t say no to.
To your success,
Kevin
Who is Dan Kennedy?
https://books.forbes.com/authors/dan-kennedy/
Unsubscribe:
https://marketersmentor.com/unsubscribe.php?d=techweapon01.com